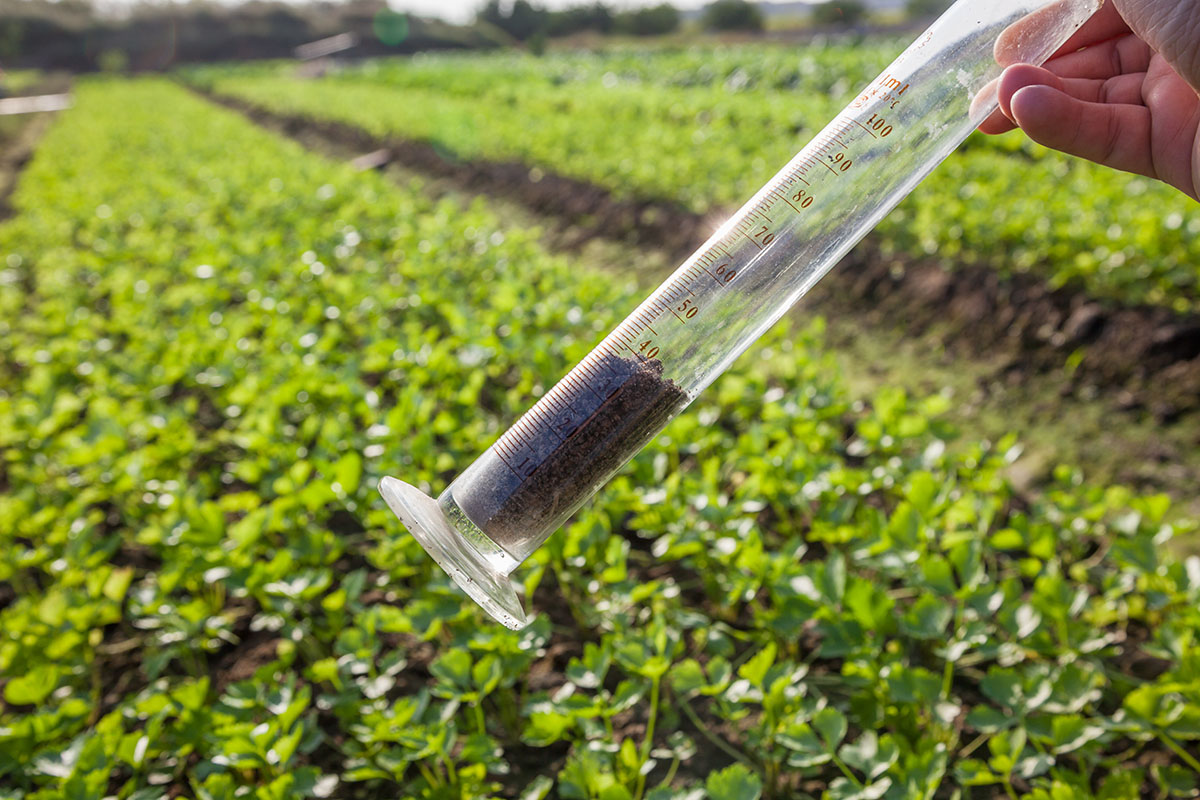
Urban soils are particularly prone to contamination. 50 years ago, your yard could have belonged to a farmer, who, perhaps not knowing any better, disposed of old bottles of anti-freeze or contaminated diesel in a hole out behind the tractor garage. Or perhaps the remains of a fallen down outbuilding, long ago coated in lead-based paint, was buried on your property buy a lazy contractor when your subdivision was built.
For those wanting to garden on non-residential urban property – school yards, church grounds, parks, commercial areas, vacant lots – the likelihood of contamination is even higher. There is no telling what sort of past activities took place there, all visible signs of which have disappeared. Prior the 1970s, environmental rules were very lax, and it was not uncommon for all sorts of hazardous chemicals to be dumped at any location where they were used. Many such chemicals persist in the soil for decades, if not longer.
The good news is that if the property was redeveloped (any significant new construction, demolition, or change of use) since environmental laws tightened, it would have had to go through a strict assessment to determine if contamination was present. If anything unacceptable was found, the owner would have been forced to remediate the soil before starting construction. However, if the property has remained more or less as-is since the 1970s (or earlier), it is unlikely that anyone has ever investigated what might be lurking in the soil.
READ THE REST OF THE ARTICLE: https://modernfarmer.com/2018/06/urban-gardening-101-how-to-deal-with-contaminated-soil/